Manufacturing
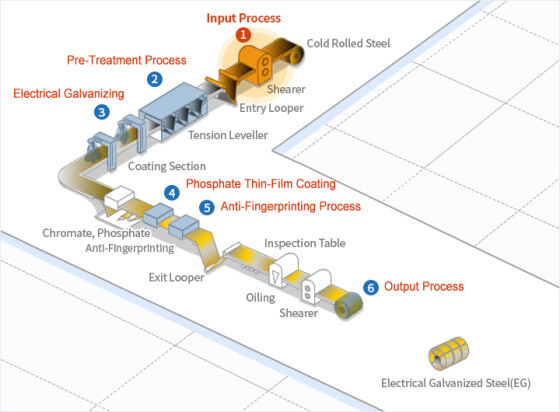
 Electrical Galvanized Steel1. lnput Process: Equipment at the entry point of the electrogalvanizing line consists of a pay-off reel, a shearing M/C, a welding M/C, a looper and a tension leveler. The pay-off reel transports stacked or cold rolled steel materials to the shearing machine which cuts and connects them in preparation for welding. Then comes the welding.
Electrical Galvanized Steel1. lnput Process: Equipment at the entry point of the electrogalvanizing line consists of a pay-off reel, a shearing M/C, a welding M/C, a looper and a tension leveler. The pay-off reel transports stacked or cold rolled steel materials to the shearing machine which cuts and connects them in preparation for welding. Then comes the welding.2. Pre-Treatment Process: An electrolytic cleaning line consists of an electrolysis tank, an acid bath and a rinse tank to remove contaminants and oxide films from the surface of the steel before electroplating.
3. Electrical Galvanizing: The CAROSEL method, among other electric galvanizing, involves the plating of one side at a time by means of a conductor roll. This process produces two-sided, single-sided, differential-sided plated sheets. There is also the horizontal type where two sides of a sheet are plated at the same time to produce a two-sided plated sheet.
4. Phosphate Thin-Film Coating: A phosphate thin-film is applied to the surface of the zinc layer through chemical or electrochemical reactions. The film is intended to provide temporary anti-corrosion protection and to generate a secure painting substrate.
5. Anti-Fingerprinting Process: An organic, inorganic or organic-inorganic hybrid film is applied to the surface of sheet steel in order to supplement its corrosion resistance and to enhance desirable properties such as resistance to fingerprint marks and workability.
6. Output Process: The exit point of the line includes an output looper, tension reel, and an automatic packaging line to protect the products after coil winding.
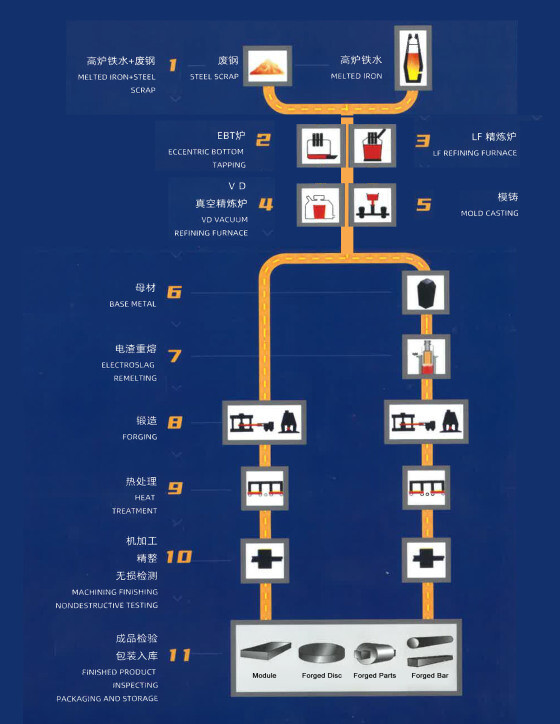
View Video Forging Steel1. Heating: Pre-forged metal starts with metal blocks called "ingots," which come in a variety of shapes and sizes depending on the part or component to be produced. These ingots are heated to a near molten state where the metal still retains its shape but can be altered easily with force.
Forging Steel1. Heating: Pre-forged metal starts with metal blocks called "ingots," which come in a variety of shapes and sizes depending on the part or component to be produced. These ingots are heated to a near molten state where the metal still retains its shape but can be altered easily with force.2. Preforming: In order to form a piece of the ingot to be pressed between the closed dies, the heated ingot is edged and blocked with a press or hammer. Edging is done to increase the working cross section and blocking is implemented to refine the shape for finish forging.
3. Finish Forging: To complete the shape, the preformed metal is forced into an impression between two dies; this is where the metal takes on the general shape of the end product. Simple items may only need one press, but more complicated items may require multiple strokes at different pressures or even different dies to design the final product.
4. Cooling: By coordinating the cooling of the metal, forgers can increase the strength of the final product by deforming and optimizing the grain flow within the metal. A aspect of impression die forging is the "flash," which is the excess metal that flows outside of the dies. The flash cools and hardens rapidly causing it to be stronger than the metal in the dies. This forces the metal in the dies to completely fill any cavities.
5. Finishing: Once a forged product has gone through the pressing process, trimming and other surface treatment operations are performed in order to improve the dimensional accuracy of the forged product. Surface treatment can be completed to enhance corrosion resistance and improve the appearance of the finished forged product.
View Video

Consulting Bulk Order Discounts
Jiancheng Steel is committed to providing the most reliable and satisfactory steel and metal product solutions to global users.